How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone piloting, covering everything from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to exploring advanced features and navigating legal regulations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take flight responsibly.
We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone mechanics, explaining the functions of key components like propellers, motors, and flight controllers. We’ll also cover essential safety protocols, including pre-flight inspections, airspace awareness, and emergency procedures. Beyond the basics, you’ll learn advanced techniques such as waypoint navigation, return-to-home functionality, and how to capture stunning aerial photos and videos. Finally, we’ll explore the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding drone operation to ensure your flights remain compliant and responsible.
Drone Components and Terminology

Understanding the individual components of a drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will detail the function of each major component and define common drone terms.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. These include propellers, motors, a flight controller, a battery, and a GPS module (in most cases). Each plays a vital role in enabling flight and maneuverability.
| Component | Function | Troubleshooting Tips | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and movement. | Inspect for damage before each flight; replace damaged propellers immediately. | Bent or broken propellers; imbalance leading to vibrations. |
| Motors | Spin the propellers; controlled by the flight controller. | Check motor connections; ensure proper voltage and amperage. | Motor failure; overheating; inconsistent motor performance. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes sensor data and controls motors. | Check firmware updates; recalibrate sensors if necessary. | Firmware glitches; sensor malfunctions; communication issues. |
| Battery | Powers the drone’s systems. | Check battery voltage before and after flights; store properly. | Low battery voltage; battery swelling; rapid discharge. |
| GPS Module | Provides location data for navigation and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Ensure clear sky visibility for optimal GPS signal. | Weak GPS signal; GPS signal loss. |
Common Drone Terminology
Understanding common drone terminology is essential for effective communication and safe operation. Here are some key terms:
- Yaw: Rotation around the vertical axis (spinning left or right).
- Pitch: Rotation around the lateral axis (tilting forward or backward).
- Roll: Rotation around the longitudinal axis (tilting left or right).
- Altitude Hold: Maintaining a constant altitude above ground level.
- GPS: Global Positioning System; used for location tracking and navigation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safe operating practices are paramount for preventing accidents and ensuring a successful flight. This section details essential pre-flight steps and safety guidelines.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive pre-flight check to ensure the drone is in optimal condition. This includes verifying battery levels, inspecting propellers for damage, and confirming GPS signal acquisition.
- Check battery voltage and charge level.
- Inspect propellers for damage or debris.
- Verify GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Check all connections and ensure nothing is loose.
- Review the planned flight path and ensure it is safe and legal.
- Check weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
Safe Drone Operation Best Practices
Safe drone operation requires awareness of weather conditions, airspace regulations, and emergency procedures. Always prioritize safety and responsible flying.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, snow, or fog.
- Airspace Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local and national drone regulations and obtain necessary permits or licenses.
- Emergency Procedures: Know how to perform an emergency landing and have a plan for potential malfunctions.
- Visual Line of Sight (VLOS): Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual flowchart can simplify the pre-flight inspection process. Imagine a flowchart starting with “Begin” and branching to “Battery Check,” “Propeller Inspection,” “GPS Signal Check,” and “Connections Check.” Each branch leads to a “Pass/Fail” decision point, with “Pass” leading to the next step and “Fail” requiring troubleshooting or component replacement before proceeding. The final step is “Ready for Flight.”
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvering: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding basic drone controls and maneuvers is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section will explain the basic controls and provide step-by-step instructions for performing fundamental maneuvers.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones utilize two joysticks or control sticks for maneuvering. One joystick typically controls the drone’s altitude and direction (forward/backward, left/right), while the other controls yaw (rotation) and pitch/roll (tilting). Buttons are commonly used for functions like taking off, landing, and activating specific flight modes.
Basic Maneuvers
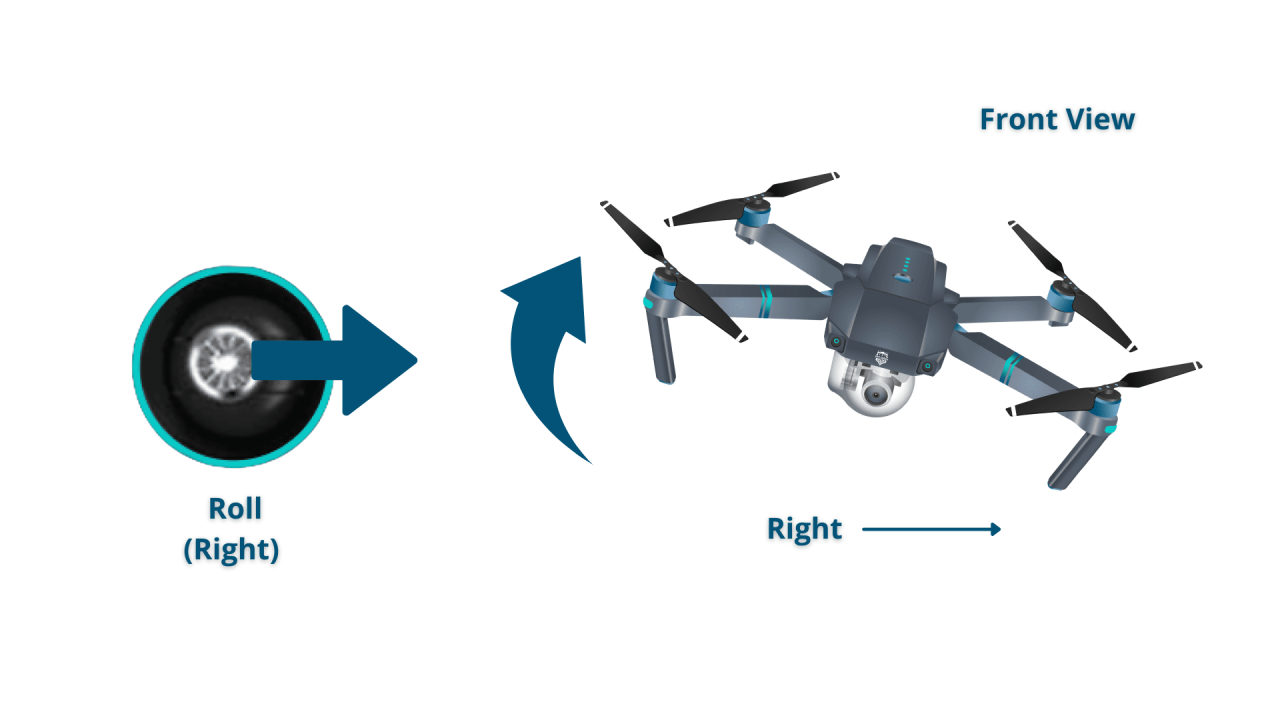
Mastering basic maneuvers is crucial for safe drone operation. These maneuvers include taking off, landing, hovering, and moving in different directions. Each maneuver requires a specific combination of joystick movements.
- Taking Off: Gently push the throttle stick upwards to initiate ascent.
- Landing: Slowly lower the throttle stick to descend and gently set the drone down.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle position to keep the drone at a constant altitude.
- Moving in Different Directions: Use the directional stick to move the drone forward, backward, left, or right.
Altitude Control and Stability
Maintaining a stable position and controlling the drone’s altitude are critical skills. This involves using the throttle stick to adjust altitude and utilizing features like altitude hold to maintain a constant height.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful planning and practice; a comprehensive guide on this topic can be found at how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and understanding the technology.
Advanced Drone Features and Techniques
Beyond basic controls, drones offer advanced features and techniques that enhance capabilities and enable more complex operations. This section explores these features and techniques.
Advanced Drone Features
Advanced features such as waypoint navigation, Return-to-Home (RTH), and obstacle avoidance significantly improve drone operation. Waypoint navigation allows for pre-programmed flight paths, RTH ensures the drone automatically returns to its starting point, and obstacle avoidance helps prevent collisions.
Advanced Flight Techniques, How to operate a drone
Smooth and precise drone control requires practice and understanding of advanced techniques such as camera stabilization and cinematic shots. Camera stabilization minimizes shake and produces smoother footage, while cinematic shots involve creative camera movements to enhance visual appeal.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and automation. For example, “Beginner Mode” might limit speed and responsiveness, while “Sport Mode” allows for more aggressive maneuvers. Choosing the appropriate flight mode depends on the pilot’s skill level and the intended task.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. This section details the process of capturing high-quality aerial media.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving professional-looking drone footage involves understanding factors such as lighting, composition, and camera settings. Proper lighting is crucial for well-exposed images, while composition involves arranging elements within the frame to create visually appealing images. Camera settings, such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, impact image quality and should be adjusted accordingly.
Tips for Professional-Looking Drone Footage
- Use the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives.
- Utilize smooth, controlled movements to avoid shaky footage.
- Edit your footage to enhance its visual appeal.
- Practice composition rules like the rule of thirds.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued functionality. This section provides guidance on both aspects.
Drone Maintenance Schedule

Establish a regular maintenance schedule to inspect and clean your drone. This should include checking propellers, motors, and the battery for any signs of wear and tear. Cleaning the drone body and sensors regularly is also recommended.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Common drone problems include battery issues, motor malfunctions, and GPS signal loss. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more serious damage.
- Battery Issues: Check battery voltage and charge; consider replacing aged batteries.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motor connections; replace damaged motors.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear sky visibility; recalibrate GPS if necessary.
Replacing Damaged Components
Replacing damaged components requires careful attention to detail and following the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure you use genuine replacement parts to maintain the drone’s integrity.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to relevant laws and regulations. This section highlights key legal and regulatory considerations.
Drone Regulations and Licensing
Drone regulations vary by location. Research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area, including any licensing requirements or registration processes. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal action.
Privacy and Restricted Airspace
Respecting privacy is crucial when operating a drone. Avoid flying over private property without permission and be mindful of recording individuals without their consent. Furthermore, be aware of restricted airspace, such as airports and military installations, and avoid flying in these areas.
Consequences of Violating Drone Laws
Violating drone laws can have serious consequences, including hefty fines, equipment confiscation, and even criminal charges. Responsible drone operation is essential to avoid legal repercussions.
Drone Flight Simulation and Practice
Drone simulators offer a safe and controlled environment to practice flying skills before operating a real drone. This section explores the benefits of using drone simulators.
Benefits of Drone Simulators
Drone simulators provide a risk-free way to learn and improve drone piloting skills. Practicing in a simulated environment helps develop muscle memory and build confidence before flying a real drone, minimizing the risk of accidents or damage.
Choosing and Using Drone Simulation Software
Several drone simulation software options are available, offering varying levels of realism and features. Consider factors such as realism, control interface, and available aircraft models when choosing software. Familiarize yourself with the software’s controls and features before starting practice sessions.
Practicing in a Safe Environment
Practicing in a simulated environment allows pilots to make mistakes without consequences. This risk-free environment is invaluable for learning complex maneuvers and developing proficiency before venturing into real-world flights.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical understanding with practical skill. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to handle your drone safely and confidently. Remember that consistent practice, coupled with a thorough understanding of safety procedures and regulations, is key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
So, take to the skies responsibly, and enjoy the unparalleled perspectives that drone technology offers!
Essential FAQs
What is the best drone for beginners?
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is learning about pre-flight checks and procedures, which are essential for safe and effective operation. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone to ensure you’re well-prepared before your first flight.
Mastering these skills will allow you to confidently and responsibly operate your drone.
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring simplified controls and robust safety features. Research models with good reviews and consider factors like flight time, camera quality, and ease of use.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies considerably depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight style). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will attempt to guide the drone back to its takeoff point. However, practice emergency landing procedures in case RTH fails.
How do I clean my drone?
Use a soft brush and slightly damp cloth to clean the drone body. Avoid using harsh chemicals or excessive water. Consult your drone’s manual for specific cleaning instructions.
